![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com
On Inheriting and Sharing Property Values

There are many ways to share properties, but what would it look like to inherit and use any parent property value on a child?
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

There are many ways to share properties, but what would it look like to inherit and use any parent property value on a child?
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

Sketch probably didn’t “have” to redesign its UI to line up with macOS Tahoe, but a big part of its appeal is the fact that it feels like it totally belongs to the Mac.
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com
Is there really a difference between using :not(:open) and :closed? As always, it depends. Sunkanmi Fafowora explains why :closed is currently not a thing.
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

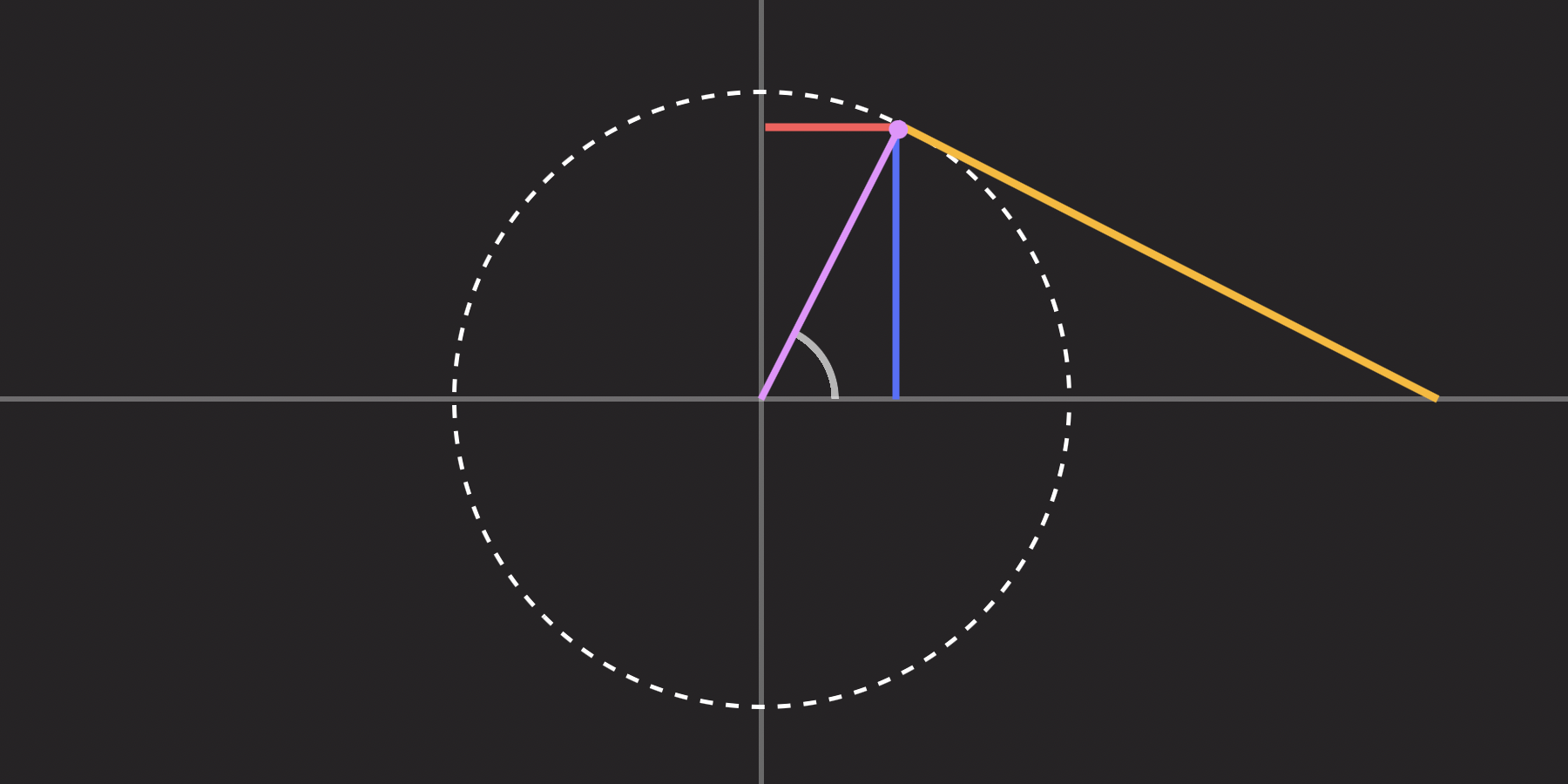
If we have a ratio that represents the sine, cosine or tangent of an angle, how can we get the original angle? This is where inverse trigonometric functions come in!
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

The extremely new framework that caught lots of attention will continue as a personal project.
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

CSS Masonry shaping up now that the CSSWG has landed on display: grid-lanes to trigger the layout switch.
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

Bramus shares that Chrome Canary no longer forces CSS animations using width and height properties to run on the main …
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

Being able to use the range syntax with container style queries — which we can do starting with Chrome 142 — means that we can compare literal numeric values as well as numeric values tokenized by custom properties or the attr() function.
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

A few links about headings that I’ve had stored under my top hat.
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

Why should you use a semantic <button> instead of a generic <div>? Accessibility, right? By how exactly does it help accessibility?
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com
Last time, we discussed that, sadly, according to the State of CSS 2025 survey, trigonometric functions are deemed the “Most Hated” …
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

On mobile, people can lose their sense of context and can’t easily tell where a section begins or ends. Good small-screen design can help orient them using a variety of techniques.
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

Can we use the <details> element as the foundation for a tabbed interface? Why yes, we can!
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com
When we change an element’s intrinsic sizing, its children are affected, too. This is something we can use to our advantage.
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com
A thorough but approachable lesson on JavaScript expressions excerpted JavaScript For Everyone, a complete online course offered by our friends at Piccalilli.
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

Honeypots are fields that developers use to prevent spam submissions. They still work in 2025. But you got to set a couple of tricks in place so spambots can’t detect your honeypot field.
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com
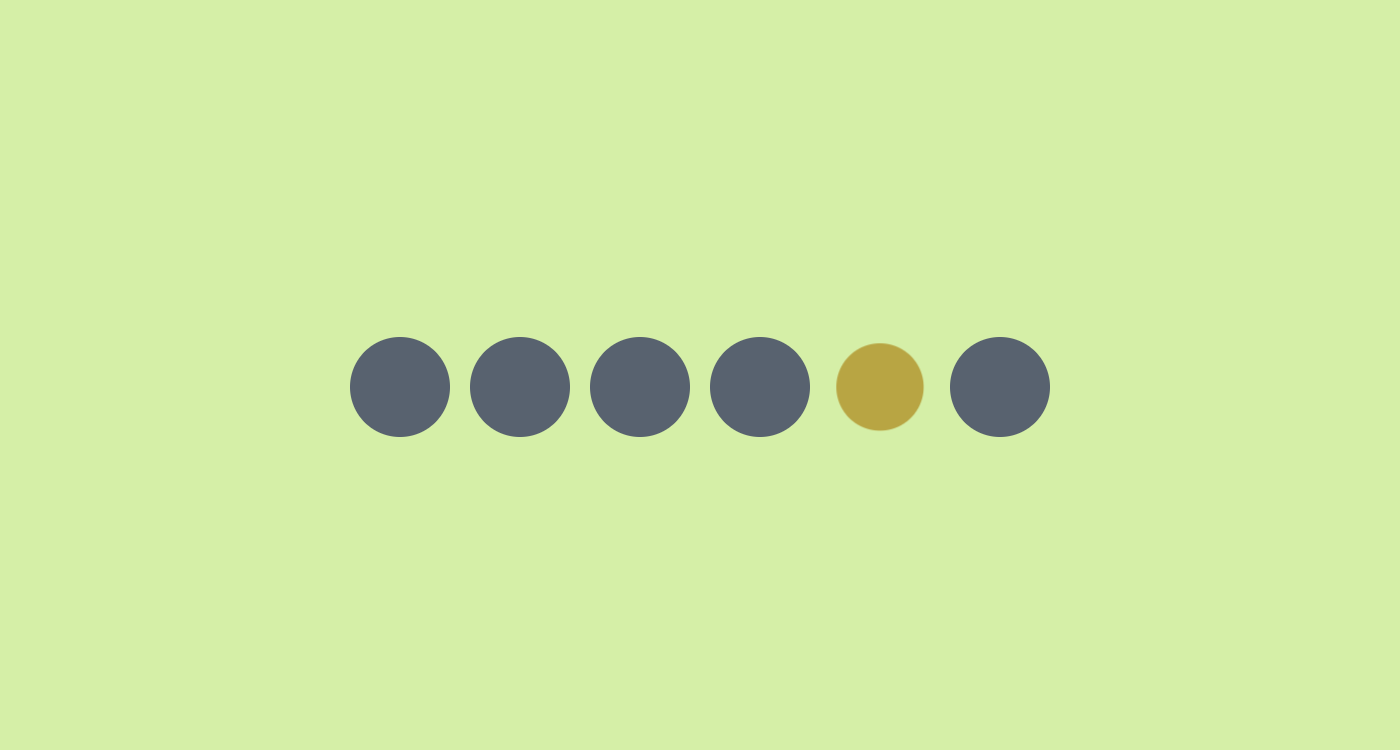
Let’s suppose you have N elements with the same animation that should animate sequentially. Modern CSS makes this easy and it works for any number of items!
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

What can CSS Masonry discussions teach us about the development of new CSS features? What is the CSSWG’s role? What influence do browsers have? What can learn from the way past features evolved?
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

The TL;DR is that stretch does the same thing as declaring 100%, but ignores padding when looking at the available space.
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

One of our favorites, Andy Clarke, on the one thing keeping the CSS contrast-color() function from true glory: For my …
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

There are so many creative opportunities for using shape-outside that I’m surprised I see it used so rarely. So, how can you use it to add personality to a design? Here’s how I do it.
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

Naturally, everything looks like code when I’m staring at a blank canvas. That’s whether the canvas is paper, a screen, some Figma artboard, or what have you.
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

Alignment might be one of the more confusing (or misunderstood) parts of CSS. I love having a thorough explanation from …
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

Safari 26 adds:75 new features, 3 deprecations, and 171 other improvements. Here’s all the CSS goodness you’ll want to know about.
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

John Rhea challenged himself to recreate the fancy button using the new CSS shape() function sprinkled with animation to get things pretty close.
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com
A working draft for CSS Environment Variables is posted. Same concept as var(), but env() is a “global” variable at …
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

Starting in Chrome 140, we’ll be able to calculate numeric values with mixed data types. Sounds small, but Amit demonstrates how big a deal this is, calling it Computational CSS.
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com
A set of notes taken from Eric Bailey’s article about the use of inclusive personas and user research.
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com

Many of the Sass features we’ve grown to love have made their way into native CSS in some shape or form. So, should we still use Sass? This is how developer Jeff Bridgforth is thinking about it.
![]() css-tricks.com
css-tricks.com
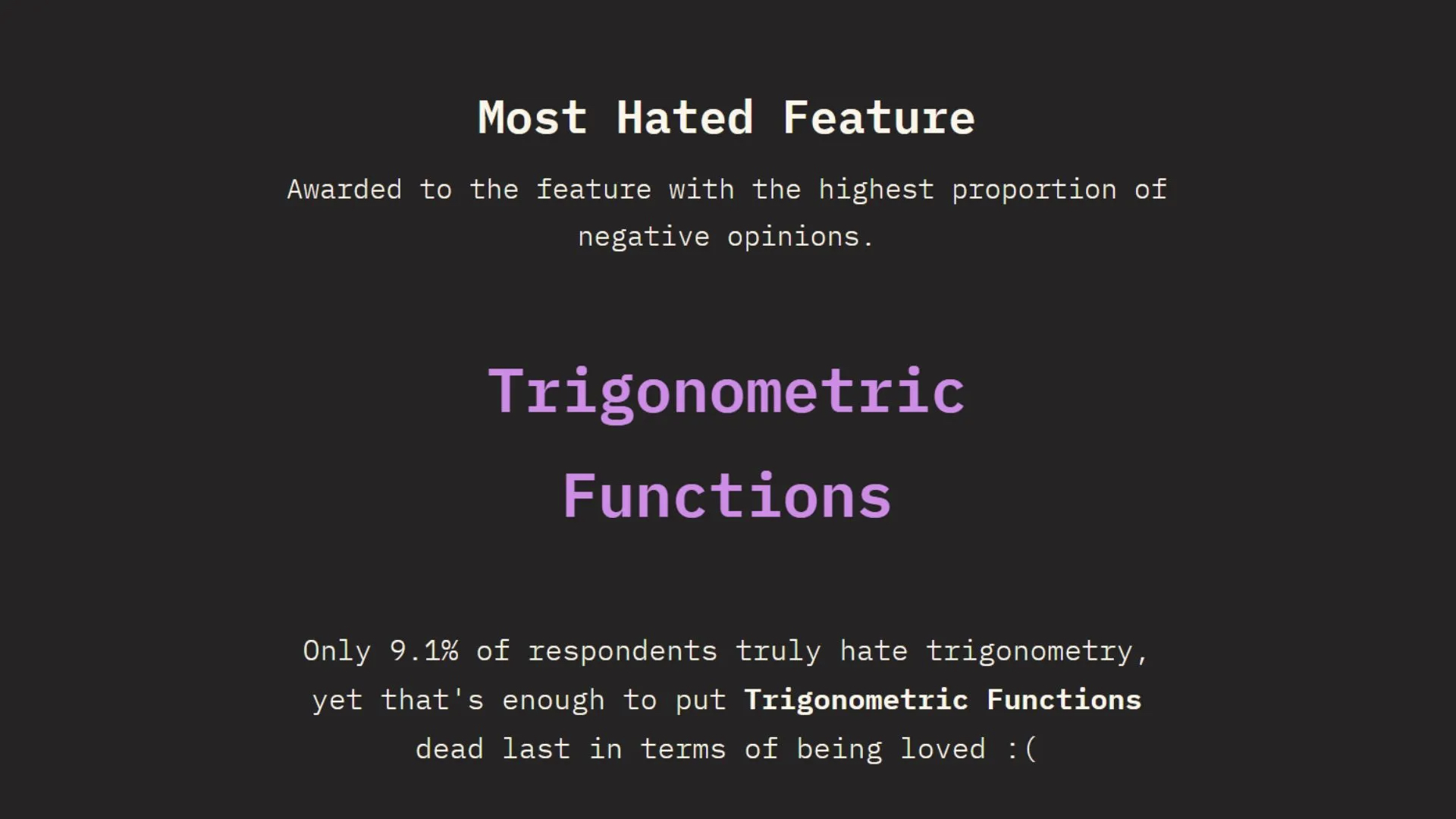
I want to look at practical uses for CSS trigonometric functions. And we’ll start with what may be the most popular functions of the “worst” feature: sin() and cos().